Music has always played a major part in human lives. Ages ago, people were introduced to different musical instruments based on strings and percussion; however, as technology further advanced, so did the music. We were introduced to new ways of playing and creating music even without the need for the classic instruments.
Today, we can even create our music through our phones or tablets; however, for those who are serious with music production, several devices are essential such as the synthesizer and other modern-day instruments. However, one truly stands out as the frontrunner for the change of music that we listen to today, and that is the arpeggiator.
To fully understand what is an Arpeggiator, we need to break down first the basics of what an arpeggio is about and what it does in music. The word arpeggio comes from the Italian term arpeggiate, that means to play on a harp. This is because harps are good when playing chords that are arpeggiated. An arpeggio is a term used for a broken chord when the notes in the chord are played one at a time instead of being played at the same time. In contrast, when playing a chord, the notes are played at the same time and produce a well-tuned sound.
One would think, what is the purpose of arpeggios in music? Arpeggios create a flowing sound and are used for speed when playing music. It adds a lot of diversity of the music through means of improvisation. This technique is commonly used in solos that make the musician own the music they are playing. Arpeggios are also very important as it is a form of repetitive exercise that will create great muscle memory for the musician.
A musician with good muscle memory will be able to recognize patterns in music and will also help you understand music composition better. As a road to develop your music composition skills, practicing arpeggios is highly advised.
Arpeggios are a great musical technique that enhances the sound made and is a great addition to an accompaniment. Most of the time, arpeggios are mastered to develop a certain technique. A good example of this is a song by Coldplay called Clocks, especially during the intro.
What is an Arpeggiator, and what is its function?
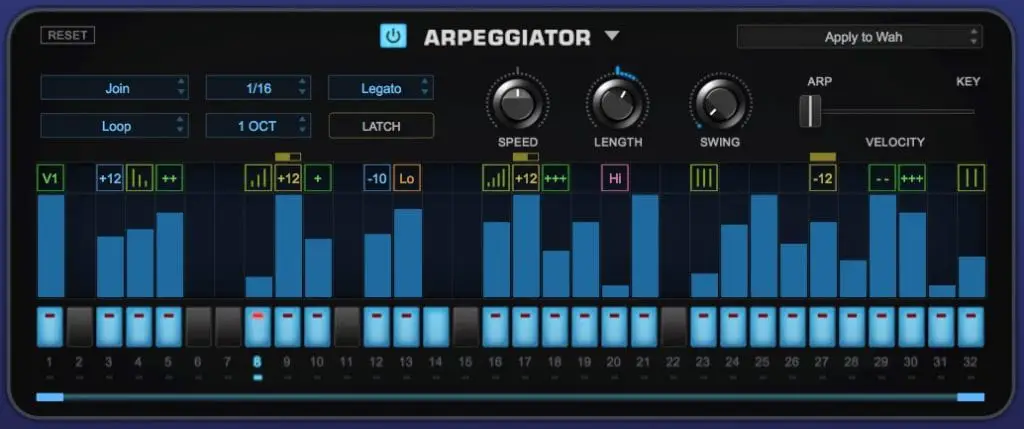
An Arpeggiator or arp in common terms is simply an automated version of an arpeggio. It is commonly found in synthesizers and would emulate the break down of the chords into simple notes to play out a tune. Most arpeggiators are served as a major feature in a synthesizer, and while it does have a very complex-sounding name, it has a more straightforward role in the development of music.
Music is usually played with chords; however, in different cases, one would have to break down the chords into simpler notes to create a different pattern that is far more complex than the progression of chords. Think of it as a guitar player plucking out the strings instead of strumming it, thus creating a simple yet equally complex pattern of notes and sounds.
An arpeggiator can provide synth players with an easy method to play these complex parts and provide a very creative output. This feature simply creates a pattern or an arpeggio then played with a tempo. The player would have to hold the note and somehow record the note and simply hit the chord again for the pattern to continually play until a new note or chord is played. This pattern goes on until the player decides to take another course or tempo.
The best example of music that heavily features an arpeggiator is that of Daft Punk in the movie Tron. Most electronic music in the 80s and even up to this day are heavily influenced by the technique and is commonly featured in such genre.
History of the Arp

The history of the arp began in the late 1960s to the early 1970s when synthesizers were slowly becoming a great addition to music. It wasn’t during the late 1980s until the mid-1990s that synthesizers were an inevitable part or feature of songs. This is because arpeggiator sequences have been incorporated in modern dance music.
Early arpeggiators simply use a cycle of notes that either has the pitch up or down and are played in different lengths. Modern-day arpeggiators offer more options and features with the option to switch up and down modes and a random mode to creatively change the tempo. Modern arps have far more complex patterns or presets, and players can even program their own.
Portable synthesizers often have these features, while workstations often have more complex arpeggiators with programs that have different layers of sounds with different patterns. Hence, disc jockeys or DJs and music producers can have a creative output when they are given more time on their workstations.
Different Parameters of an Arpeggiator

There are four main basic parameters of an arpeggiator that will allow the individual notes to be played automatically in different patterns. Up, Down, Up/Down, and Random are the basic parameters and that these should be present for any arpeggiator. However, there are also a lot of modern-day features used in advanced arpeggiators today. This include:
- Manual – which follows the order of the notes in the chord once it is triggered.
- Poly – the chord is played repeatedly in a rhythmic pattern.
- Step Rate – the rate at which the arpeggiator uses the unit of time to perform the pattern, such as 1/8, 1/16.
- Latch – a very common feature in modern arpeggiators that allow the arpeggiated sequence to be played continuously even if the player has stopped sustaining the chord. This allows the chord to be layered by another chord to produce a more creative output.
How to Use an Arpeggiator

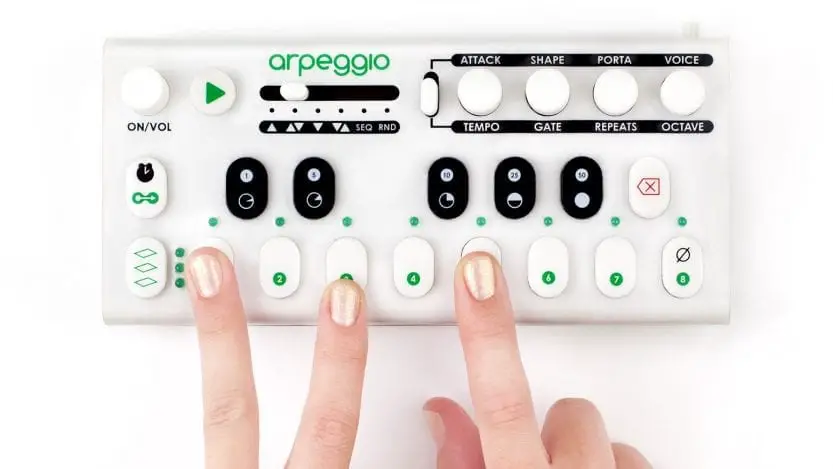
While arpeggiators are different individually, the concept of using them is typically the same. First, turn on the arpeggiator and play a chord on the piano or keyboard. You should be able to hear the notes being arpeggiated.
When you try to play a single note, you will notice that the note is being repeated in a sequence. Add another note, and as you press the keys, they are added to the arpeggio. When you let go of one of the keys, the note is dropped from the arpeggio while the other notes continue to play.
Take note that the arpeggiator will be playing the notes in the order that you hit the keys. The volume of the arpeggiated notes will also depend on how hard you hit the keys; hence striking the keys should be careful.
The arpeggiator will continue to play the notes in order, but it will differ according to speed, range, and direction. Depending on the arpeggiator being used, there are other features such as swing control and note length that will further enhance the groove.
Basic Features of an Arpeggiator

Arpeggiators are most of the time different from each other; however, certain parts will always remain the same. While these features do not necessarily make a complete set, they are commonly found in most arpeggiators nowadays.
- Style – this option refers to the type of sequence for the notes. This is where Up, Down, Up/Down, and Random option is usually found. Other options are added depending on the brand.
- Groove – this usually refers to the type of groove that will be applied to the sequence or pattern.
- Hold – as the option dictates, this allows the player to hold the latest note that is being played. The pattern will continue to repeat until a new note is introduced to the pattern.
- Sync – refers to the speed of arpeggiation. This is where the player can choose the rate between 1/8. 1/16, and so on.
- Retrigger – usually refers to the resetting the pattern to the beginning. Depending on the hardware or brand, it also features an option to retrigger if there are any new notes introduced to the pattern or if there the beat is in a loop.
- Repeats – refers to the times the pattern is repeated.
- Offset – allows the player to shift the pattern of notes depending on the number of steps being set.
- Gate – portrays the length of the notes within the pattern.
Benefits of Using Arpeggiators
Arpeggiators are a great tool for live performers. It showcases a lot of the player’s talents in improvisation. However, aside from the spontaneity it provides, there are also other benefits that arpeggiators cater to during a performance or production.
First, the arpeggiator allows the sequencing of the chords and notes to be played on and on, whereas other instruments will make it more difficult. The progression of the performance becomes more tedious as the sequence overlap. With the help of the arpeggiator, the sequences are easily given attention to, and the performance becomes easy-flowing for the player. Arpeggiators usually have features like gate length that helps make the performance more interesting.
Another benefit of using arpeggiators is that you can basically add or remove notes as you like and even put them in a different order to create a new sound or a new iteration of the sound that you have just created. The playback mechanic also allows you to layer even more sound, but arpeggiators can dial it up and make the execution more fluid.
Sometimes, you can create your pattern; however, you also wish that it can still be improved upon or simply play around with the beat. With the help of an arpeggiator, you can implement the pattern in any way you like or even do it on other parts of a different track.
The versatility of an arpeggiator is what makes it a cut above other musical instruments. One can get a lot of work done and create sound and music in just a few minutes of inspiration instead of a ton of work from other instruments. When you already have the music in your thoughts, it can easily be transformed with the help of an arpeggiator.
Best Synthesizers for Beginners
If you want to start your journey in music, the best way to do so is to get a synthesizer that has all the features you need to create the music you want. There are a lot of software synthesizers that help you kickstart your music career; however, there is still something about a hardware instrument that will help you reach your full potential. Here are some of the best synthesizers with arpeggiators for beginners.
1. Roland Boutique D-05
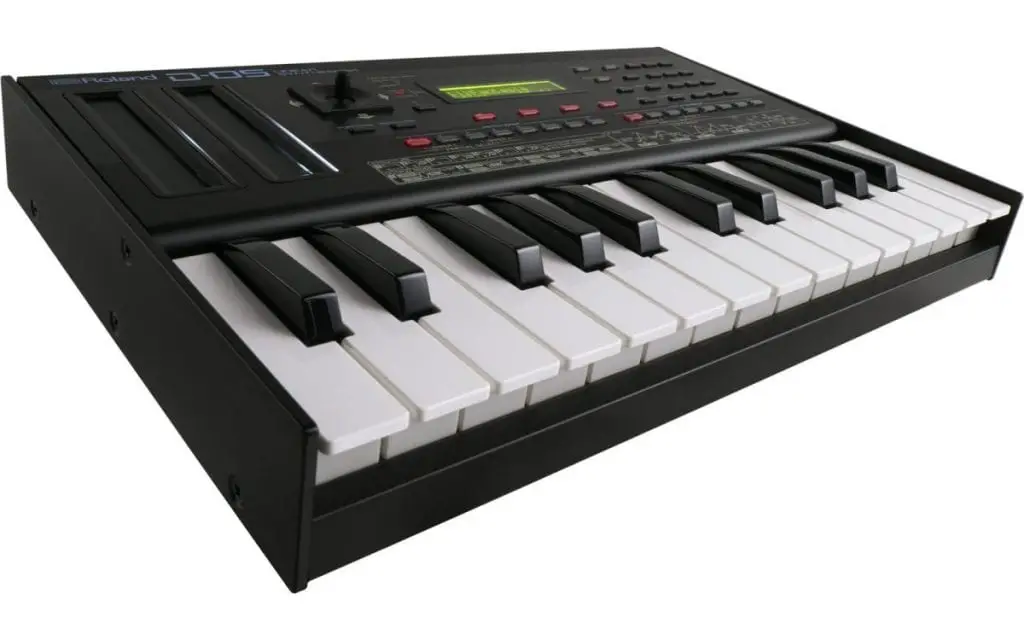

The D-05 is a classic synthesizer that offers a very 80s feel. This is because the D-05 takes its concept from the classic D-50, where it was commonly used in the 80s. In fact, the D-05 is almost the same as the D-50 in terms of its hardware and features. This is a great successor to what was once the king of synthesizers in the 80s. While it remains to be a classic, it also offers great features such as a 64-step polyphonic program and a multi-mode arpeggiator. But what sets it apart from its predecessor are the presets and its ability to load even more presets.
2. Moog Grandmother

Another synthesizer that is very simple in terms of usage. this synth comes from the popular Robert Moog brand in the 60s as the first synthesizer to be commercially sold. This specific type is a semi-modular synthesizer that has a 32-note, velocity-sensitive keyboard. This multi-colored retro-styled synthesizer has an old school approach that is apt for those who want to learn more about the equipment along with arpeggiators.
Many other keyboard instruments are often fitted with arpeggiators, and throughout its long history starting in the late 1970s to the early 1990s, these popular synthesizers were used to make rapid-fire arpeggios that are the key to the success of the music. Some of these early synthesizers include the Korg Polysix, Yamaha DX-7, and the aforementioned Roland D-50. To this day, modern arpeggiators are still commonly used in music and are considered an integral part of today’s music.



